BACTERIA IMAGES
INTRODUCTION: Bacteria are the simplest ,most primitive and unicellular organisms without a true nucleus. That is why they are prokaryotic. they are placed under kingdom Monera. they are found everywhere in air,water,soil,food,inside our body etc. they lack nucleus and other cell organelles of complex cellslike plants,they possess a cell wall. each bacterial cell has its nuclear material in the form of a single chromosome which is not enclosed in a nuclear membrane.
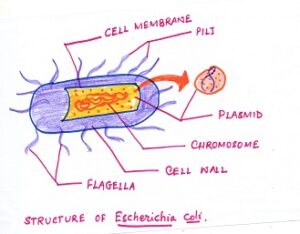
STRUCTURE OF BACTERIA
SIZE:
Bacteria are the smallest of all living organisms. Their size is usually expressed in microns. An average spherical bacterial cell is 0.5 micrometre (µ) in diameter but most of them range from 0.2 to 2.0 micrometer (µ) in width and less than 2-10 micrometre (µ) in length. Bacillus forms vary from 0.3 to 15 micrometer (µ) in length and from 0.2 2.0 micrometre (µ in width. A single drop liquid may contain about 50 million bacteria.
SHAPE
According to shape bacteria are of four types.
SHAPE OF BACTERIA
| SHAPE OF BACTERIA | SHAPE | CHARACTERISTICS | DIAGRAM |
| COCCUS
(plural: cocci) |
Spherical shaped | These may be present in clusters (Staphylococci) like a bunch of grapes. Sometimes form long chain(Streptococci)
or in pairs (Diplococci) |
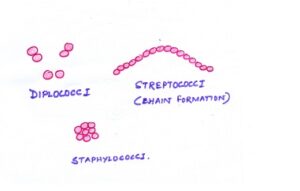 |
| BACILLUS
(plural: bacilli) |
Rod shaped | These may be present as a single (Escherichia coli)
or in chains (Bacillus anthracis) |
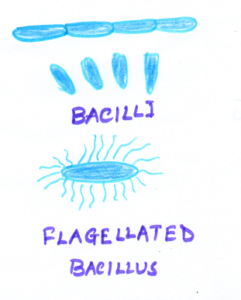 |
| SPIRILLUM
(plural: spirilla) |
Spiral or curved shaped | These bacteria may have one or more flagella at the end of their bodies (Leptospira spirillum) |  |
| VIBRIO | Comma shaped | The body is curved with only one flagellum (Vibrio cholera) |  |
STRUCTURE OF BACTERIUM
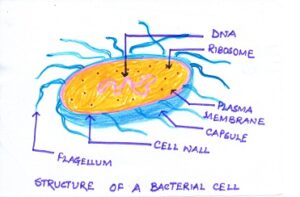
*Each bacteria is a simple cell.
*It contains protoplast which is a living substance.
* Bacteria cell is surrounded by a non-living rigid cell wall.
* Bacteria cell wall contains peptidoglycan . It is not cellulose.
*Beneath the cell wall is a thin membrane which surrounds the cytoplasm.
*It does not contain membrane bound organelles like chloroplasts, mitochondria, golgi body and endoplasmic reticulum.
* The chromatin material is in the form of a single molecule of circular DNA attached to the cell membrane. It is not enclosed in a nuclear membrane.
* Nucleoid is the single circular DNA molecule which is the genetic material present in the centre of the cell.
* Some bacteria have a slimy protective layer called capsule outside the cell wall.
*This capsule helps bacteria to remain dormant during unfavourable conditions.
*Ribosomes and plasmid which is the smaller ring of DNA present in the cytoplasm.
*Ribosomes help in protein synthesis.
METABOLIC ACTIVITY OF BACTERIA
MOVEMENT: Most bacteria are immotile i.e. cannot move on their own. They are passively transported by wind , water or simply by contact. Majority of cocci are non-motile. Some Bacteria such as bacilli and spirilla can move by the lashing movement of whip- like flagella in a liquid or watery medium. Some of them have a single flagellum at one end, while bacterium like Salmonella have
flagella all over the body.
NUTRITION: Most bacteria do not have chlorophyll. Nutrition in bacteria may be autotrophic or heterotrophic.
NUTRITION IN BACTERIA
| TYPE OF NUTRITION | SUBDIVISION | CHARACTERISTICS |
| 1)Autotrophic nutrition | i) Photosynthetic bacteria
ii)Chemosynthetic bacteria |
It contains bacteriochlorophyll and produces food material using light energy e.g. green sulphur bacteria.
This type of bacteria obtain energy by oxidizing inorganic compounds e.g. sulphur bacteria. |
| 2)Heterotrophic nutrition | i)Saprophytic nutrition
ii)decaying matter |
In this type of nutrition bacteria obtain food from perishable organic dead and decaying matter.
In this nutrition bacteria can get food from other living organism (HOST)gets shelter on the host e.g. Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
|
HETEROTROPHIC NUTRITION:
a)Saprophytic nutrition- In this nutrition bacteria obtain food from dead and decaying organisms.
- b) Parasitic nutrition- In this nutrition bacteria obtain food from other living organisms.
In heterotrophic nutrition bacteria secrete enzymes to make food material soluble which is then absorbed by the bacterial cell. Most of the heterotrophic bacteria cause diseases to the hosts.
RESPIRATION OF BACTERIA
According to the requirements of oxygen in respiration bacteria may be divided into two types:
- a) Aerobic bacteria:- They respire by utilising oxygen. By this process glucose is completely oxidised.
- b) Anaerobic bacteria:- Some bacteria respire in absence of oxygen. We can get many useful products by utilising anaerobic process.
PRODUCTION OF ENERGY DURING RESPIRATION:
Complete oxidation of food molecules during aerobic respiration results in the production of comparatively more energy (683kcal) and this is happening in aerobic respiration.
Partial breakdown of food molecules during anaerobic respiration results in the production of less energy (50 kcal ).
REPRODUCTION OF BACTERIA
- a) Asexual reproduction:- In bacteria reproduction rakes place mostly by asexul processes . It is of various types.
- i) Binary fission: It is very much popular among bacteria. Theoretically one fact can be shared that ” under ideal conditions, some bacteria divide at a rapid rate. A single bacterium cell would produce 281,514,871,750,658 bacteria at the end of 24 hours”. However, it never happens in nature due to accumulation of toxins in the medium and depletion in food supply.
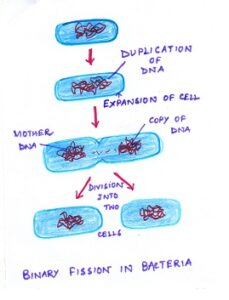
Binary fission takes place by simple mitotic division. In this process a fully grown bacterial cell divides into two identical cells by a constriction in the cell wall. The two resulting bacteria get separated and after reaching maturity redivide. In certain bacteria, the divided cells do not separate but remain attached giving rise to chains or colonies. During fission, bacteria divide into two. Cell division is preceded by duplication of the DNA. The bacterium grows and it’s nucleus enlarges due to DNA duplication. The two DNA are pulled apart to two sides. It is generally happened in favourable conditions.
- ii) Spore or Endospore formation:- Endospores are formed in a few bacteria. These are thick- walled, non- motile resistant bodies formed within the cells. These Endospores are resistant to temperature as low as ice and high as boiling water. They can withstand dry conditions and remain alive in adverse conditions for a long time. Fortunately only two of the pathogenic bacteria i.e. Tetanus causing and Anthrax causing bacteria produce Endospores.
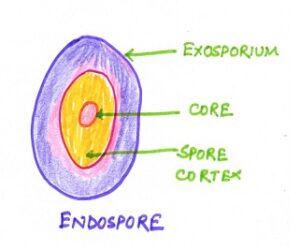
Spore formation in bacteria is not a method of reproduction but simply a method of escaping unfavorable conditions as there is no increase in the number of individuals.
Endospore formation is not a method of reproduction by bacteria. It is rather a means to protect themselves under unfavorable conditions. That time bacteria form thick- walled, non- motile resistant bodies called Endospores. These are formed within the cells. The cytoplasm of the çell condenses and then secretes a thick wall to form Endospore. It remains dormant and can tolerate high temperature, freezing temperature, pH changes, effects of chemicals. On the return of favourable conditions , each Endospore germinate to form a single bacterial cell.
- B) SEXUAL REPRODUCTION:- It occurs in bacteria through conjugation. This is an unusual form of reproduction in bacteria. During conjugation bridges are formed between two cells. Exchange of genetic material is occurred through the bridge. e.g. Escherichia coli . The new individual divideds and redivides to form new daughter cells .

thank you very much