PLANT PHYSIOLOGY
EXPERIMENTS ON PLANT PHYSIOLOGY (FUNDAMENTALS OF PLANT PHYSIOLOGY)
INTRODUCTION: Plants perform various functions to live properly like photosynthesis, respiration, transpiration etc. Here are some of the experiments on crop physiology which are done to show those physiological functions theoretically. Experiments on transpiration and photosynthesis are mainly discussed.
EXPERIMENTS ON TRANSPIRATION
EXPERIMENT – I ( FUNDAMENTALS OF PLANT PHYSIOLOGY )
OBJECTIVE: To measure rate of water uptake using a simple potometer.
REQUIREMENT: a) syringe
b) leafy shoot
c) rubber tubing
d) capillary tube with measuring scale
e) conical flask with water
f) 3 way tap

PROCEDURE IN CROP PHYSIOLOGY:
A leafy shoot was taken and it’s cut end was pushed into the rubber tubing as far as possible.
The rubber tube was attached to the capillary tube.
The 3 way tap was fixed in the middle of the rubber tube.
The 3 way tap in a potometer blocks only one way at a time, keeping the other ways open.
The syringe was filled with water and attached to it to the side arm of the 3 way tap.
The tap was turned downward at (A) position and the syringe is pressed until water comes out of the rubber tubing at the top.
Then the tap was turned upward at (B) position and the syringe was pressed till the water comes out of the bottom of the capillary.
Finally the tap was turned horizontally at (C) position and kept the set up in sunlight to observe.
The initial reading was taken. The water column was below the start of scale.
OBSERVATION
- As the shoot transpires, it will draw water into the capillary tube. The level can be seen to rise. In every 5 minutes the distance moved by the water column is recorded.
- Next the tap is turns up and the water column is sent to the bottom of the capillary. Then the tap is turned horizontally (C) again and another measurement of the rate of uptake of water after every 5 minutes are made.
INFERENCE: In this way average of three readings are obtained and rate of water uptake can be measured.
EXPERIMENT – 2 ON FUNDAMENTALS OF PLANT PHYSIOLOGY
OBJECTIVE: Study of transpiration through the upper and lower surface of a leaf using cobalt chloride paper for crop mphysiology
REQUIREMENT:
- Potted plant
- Two sheets of filter paper of same size.
- 15% cobalt chloride solution.
- Paper clips

PROCEDURE: ( cobalt chloride paper leaf experiment)
- Sheets of filter paper are dipped in 15% cobalt chloride solution.
- This paper will turn pink in colour.
- It is dried in a desiccator or kept it in seen for about an hour.
- After drying, this pink paper turns blue.
- These blue papers are cut into two rectangular pieces.
- One paper is fixed on the upper surface and another paper is fixed on the lower surface of leaf with the help of paper chips.
- This set up is made air tight by applying Vaseline at the edges.
- The set up is kept for several hours.
OBSERVATION : The cobalt chloride papers turn pink in colour. The time taken is recorded on both side separately. It has been observed that cobalt chloride paper on upper suface took more turn pink. Cobalt chloride paper on lower surface took less time to turn pink.
CONCLUSION : It is proved that upper surface has less stomata so less transpiration takes place, that is why more time was needed to turn cobalt chloride paper pink. Lower surface has more stomata so more transpiration takes place that is why less time was needed to turn cobalt chloride paper pink.
EXPERIMENTS ON PHOTOSYNTHESIS IN CROP PHYSIOLOGY
First plants should not have starch in it’s leaves , before the experiment is started. The leaves of a potted plant may be destarched by leaving it in a dark place for 2-3 days.
EXPERIMENT-3
OBJECTIVE: To test a leaf for presence of starch.
REQUIREMENT:
- Potted plant
- Beaker
- Methylated spirit
- Test tubes.
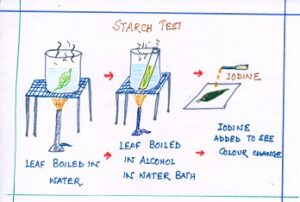
PROCEDURE:
- Potted plant is kept 3-4 hours in sunlight .
- Fresh green leaf is detached from plant.
- The leaf is dropped in boiling water.
- By this process protoplasm and enzymes are killed, so no further chemical changes take place.
- By boiling cell will be more permeable to water.
- After that the leaf is boiled in test tube containing the methylated spirit in a water bath till it becomes colourless due to removal of chlorophyll.
- Leaf has become brittle and hard.
- Again the leaf is placed in boiling water to make it soft again.
- Then the soft leaf is spreaded flat on a white surface like petridish and few drops of iodine solution are poured on the leaf surface.
OBSERVATION: The leaf will turn blue black.
INFERENCE: Iodine turns blue black in presence of starch. So the leaf contains starch.
EXPERIMENT 4 ON FUNDAMENTALS OF PLANT PHYSIOLOGY
OBJECTIVE: Carbon-dioxide is necessary for photosynthesis in crop physiology
REQUIREMENT:
- Destarched potted plant.
- Conical flask.
- Some potassium hydroxide.
- Spilt cork.
- Materials for starch test.

PROCEDURE:
- Some potassium hydroxide is kept in conical flask.
- One leaf of destarched plant is inserted inside the conical flask.
- The flask is made air tight by a split cork.
- The set up is left in sunlight for few hours.
- After few hours the leaf is removed from flask.
- Another exposed leaf from same plant is taken.
- Both the leaves are tested for presence of starch.
OBSERVATION :
- The leaf in the conical flask does not turn blue black by starch test.
- But the exposed leaf will turn blue black by starch test.
INFERENCE:
The conical flask contained potassium hydroxide which absorbs carbon- dioxide. So the leaf inside the flask did not get carbon dioxide and did not perform photosynthesis so it is proved that carbon dioxide is necessary for photosynthesis.
EXPERIMENT 5
OBJECTIVE: Sunlight is necessary for photosynthesis.
REQUIREMENT:
- Potted plant which is destarched by keeping it in dark for 3-4 hours.
- Two pieces of black paper which cut simple “L” shape in it.
- Materials for starch test.

PROCEDURE:
“L” shaped cut black papers are placed on either side of one leaf by paper clip.
- This set up is kept for 4-6 hours in sunlight.
- Then the leaf is detached from the plant and test for starch test.
OBSERVATION:
The part of leaf out of black paper and inside the “L” turns blue black. Other part under the black paper does not show any colour change.
INFERENCE:
The part under black paper does not get direct sunlight. So this part does not perform photosynthesis and not produce starch. So it is proved that sunlight is necessary for photosynthesis.
EXPERIMENT 6 ON CROP PHYSIOLOGY
OBJECTIVE : Oxygen is given out during photosynthesis.
REQUIREMENT:
- Aquatic plant like Hydrilla
- Beaker
- Funnel
- Two corks
- Pond water.

PROCEDURE:
- A bunch of Hydrilla is placed in a beaker containing pond water.
- The plants are covered with a short stemmed inserted funnel.
- The level of funnel is slightly raised above the bottom with the help of two pieces of cork.
- In this way water can be freely circulated.
- A test tube filled with fully inserted over the stem of the funnel.
- The apparatus is placed in sunlight or bright light for few hours.
OBSERVATION :
Bubbles of gas are appeared from the cut ends of stems. These bubbled are risen, and collected in the test tube. The water level becomes lowered to collect gas. This collected gas is tested by introducing a glowing splinter, which will burn into flame.
CONCLUSION:
So the gas collected in test tube is oxygen. Oxygen is produced during photosynthesis it is proved.
