FLOWER STRUCTURE
DEFINITION OF GAMETES :- Flowers are the reproductive parts of plants,which are responsible for the production of gametes or sex cells ((non flowering plants).
A flower is modified shoot in which the leaves are modified into floral parts. A blossom propagates a branch from a bud in the axil of a little leaf-like structure called the bract. A bract is commonly green due to presence of chlorophyll and is a very small structure (non flowering plants).
FLOWERING PLANTS-NON FLOWERING PLANTS.
Trees that have flowers with stalk of a flower are called flowering plants or angiosperms. There are many other trees such as pine (non flowering plants),firs (non flowering plants), redwoods (non flowering plants), etc. which do not have flowers (non flowering plants) and they are called gymnosperms or naked-seeded plants (non flowering plants).
TYPICAL STRUCTURE OF A BISEXUAL FLOWER WITH STALK OF A FLOWER.
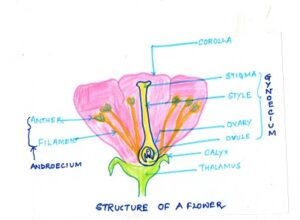
Fig#1 simplified diagram of a flower
- A) Pedicel /Stalk or stalk of a flower
Blossoms are modified as a particular branch at the tip of a stalk known as pedicel or peduncle (non flowering plants).
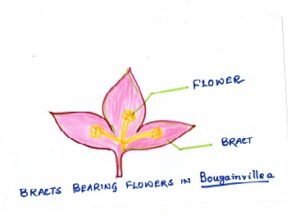
Fig#2 bracts bearing flower in Bougainvillea
In some plants such as tulip, there is only one pedicel bearing a single flower.In others , such as lilac the pedicel is branched and bears many flowers. There are some flowers ( like saffron ) without a stalk .These flowers are known as sessile flowers.
B) Receptacle ( Thalamus)
non flowering plants
The pedicel swells at its tip into a small cup-shaped pad known as receptacle or thalamus. Thalamus can be flat ,conical,concave or dome- shaped in different shapes.
All the floral whorls along with stalk of a flower arise from the receptacle. The lower part of a blossom are connected to the receptacle in rings or whorls.
C) Floral Whorls
Generally , a flower consists of four whorls,
- The calyx ( the green coloured sepals) on the outside (first whorl)
- The corolla ( coloured petals ) lying inside the calyx ( second whorl ).
- The androecium ( male parts ) enclosed by the corolla ( third whorl ) and
- The gynoecium ( female parts ) at the centre of the flower ( fourth whorl),
D ) Nectaries
Nectar is a sweet fragrant liquid secreted by most of the flowers. These flowers have the nectar secreting cells, called nectarines. Nectaries are found near the base of the pistil or or on the base of the petals. Nectar helps cross pollination .In Nasturtinum flowers ,the nectarines are very large and prominent.
( non flowering plants)
COMPLETE AND INCOMPLETE FLOWERS.
* Complete flower:- A flower which has all the four types of floral structures along with stalk of a flower namely, calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium called complete flower e.g. Hibiscus
* Incomplete flower:- A flower in which any one or more of the four floral parts are missing are called an Incomplete flower e.g.pumpkin. ( polyadelphous stamen)
ESSENTIAL AND NON-ESSENTIAL PARTS OF A FLOWER (NON FLOWERING PLANTS)
* Essential ( reproductive ) parts of a flower.:- Those parts of a flower which are directly concerned with reproduction are known as essential parts of a flower.
For example, stamens ( male parts ) and the carpels ( female parts ) are the essential parts of a flower.
*Non-essential (non-reproductive) parts of a flower) :- Those parts of a flower which directly do not take part in reproduction are called non-essential parts of a flower.They simply either protecting the reproductive parts or to make the flower attractive for pollination. For example, sepals and petals are non-essential parts of the flower.
NON ESSENTIAL PARTS OF A FLOWER (NON FLOWERING PLANTS).
CALYX.:— THE Calyx is the outermost whorl of the flower. It consists of three to five sepals,which are generally green in colour and However look like small leaves,that cover an unopened floral bud. However as in Gulmohar,they may be coloured and are known as petaloid sepals. ( polyadelphous stamen)
MODIFICATION OF CALYX.
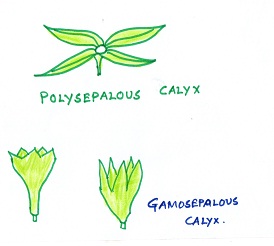
Fig#3 diagram of modification of calyx
When sepals are free from each other,as in mustard or raddish,they are known as polysepalous or they may be fused to form a cup in flowers of other plants such as china rose, (gamosepalous).
FUNCTIONS
*the calyx encloses and protects the inner whorls of the flower in the bud stage.
*Since the sepals contain chlorophyll,they can also synthesize food (photosynthesis).
*Together with petals ,they also attract the birds and insects for pollination.
2) COROLLA:- The Corolla is the most conspicuous part in the flower because it is usually white or brightly coloured. The corolla forms the second whorl from outside,inner to the calyx. This whorl is made up of petals, which are much larger than sepals. Petal number of flower is different from plant to plant.

Fig#4 diagram of modification of corolla
(non flowering plant)
MODIFICATION OF PETAL :- In some flowers the petals are green in colour,known as sepaloid petals.The petals may be separate from each other as in mustard flower ( known as polypetalous),or become partly/completely fused as in petunia ( known as gamopetalous). If the petals are completely fused, they form a corolla tube
F) FUNCTIONS :-
(non flowering plant)
* The brightly coloured corolla attracts pollinating agent causing cross pollination such as insects and birds.
*Some petals are scented with a nectary which produces sugary nectar. The insects and birds come to collect this nectar while doing so transfer pollen from one flower to another.
* The corolla encloses and protects the stamens and the pistil.
ESSENTIAL PART
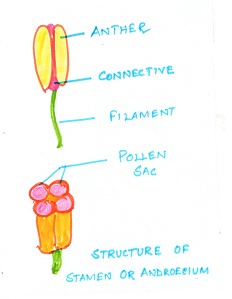
Fig#5 diagram of stamen or androecium
(non flowering plant)
A) Androecium :- The Androecium ( Andros meaning male ) forms the third whorl on the inside of the flower. Androecium consists of stamens. These are the male reproductive organs. Every stamen is comprised of a thin versatile stalk known as the filament which is fibrous, which holds the anther at its end. Anther is appended to the filament. With the help of a structure known as the connective. Each anther is two lobed. Each lobe has two pollen sacs. Thus each anther is made-up of four pollen sacs in which pollen grains are formed.Pollen grains are fine,powdery,granular structure which contain the male gametes.
Variations in the Androecium.
(NON FLOWERING PLANTS)
NUMBER OF STAMENS : The number of stamens may differ greatly in flowers of plants from different families For example, some grases have only one stamen,Mexican blood trumpet and jacarandas have four stamens and roses have several dozens.
2.POSITIONS OF STAMENS WITHIN A FLOWER :-The stamens may originate near the base of the pistil
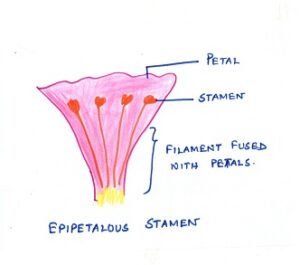
Fig#6 diagram of epipetalous stamen
or they may be fused at their base with the petals and appear to originate out of the petal. For example,in Petunia flower ,the filaments are attached with the petals and the condition is known as epipetalous. (NON FLOWERING PLANTS)
STAMENS FUSED OR FREE:-
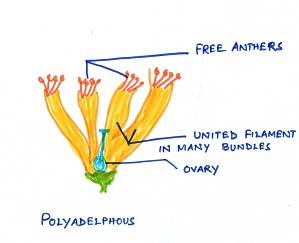
Fig#7 diagram of polyadelphous stamen
Polyadelphous: The stamens may be free and filaments are united,known as polydelphous androecium,for example mustard,Bombax etc.
Monadelphous: The filaments may be fused and anthers are free,known as monadelphous androecium,for example peas,beans and Hibiscus.
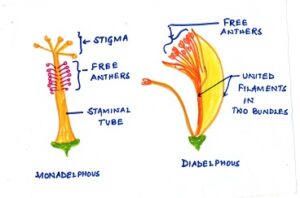
Fig#8 diagram of monadelphous and diadelphous stamen
Diadelphous : The filaments are united into two bundles and the anthers remain free,known as the diadelphous stamens,for example, peas,gram,beans.
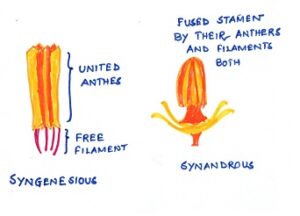
Fig#9 diagram of syngenesious stamen and synandrous stamen
Syngenesious: In some other cases as in sun-flower,the filaments are free but the anthers are united. (NON FLOWERING PLANTS)
FUNCTIONS,
* The anther produces pollen grains which contain the male reproductive cells,i.e the gametes.
* The filament carrys and supports the anther in the most proper situation for the exchange of pollen dust to transfer.
B)Gynoecium.
The gynoecium is the fourth and the innermost whorl of a flower. The gynoecium consists of ovule-bearing basic units called pistils or carpels. Collectively, carpels from the gynoecium, which is referred to as the female part of the flower because the carpels produce the female gametes. (synandrous stamen)
A flower may have one or more pistils, which consists of :
- Ovary : The basal portion is called OVARY which contains the ovules or embryo seeds. The female gametes develop in the ovule.
- Stigma : Area, where the pollen is received, is called the stigma. The stigma is the terminal part of a carpel which receives the pollen grains.
- Style : Often the stigma may be borne on a slender stalk like structure called the style. Style connects stigma to the ovary.
VARIATIONS IN THE GYNOECIUM. ( ———— are the non-essential parts of a flower)
NUMBER OF CARPELS: –Peas and beans have only a single carpel,which forms a single pistil. Such gynoecium is known as monocarpellary. It may be bicarpellary,as in mustard flower where two carpels are present.There may be more than two as in magnolia and lady’s finger,known as polycarpellary.
POSITION OF THE OVARY IN A FLOWER.
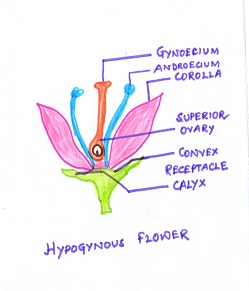
Fig#10 diagram of hypogynous flower
HYPOGYNY (THE SUPERIOR OVARY)If the ovary is attached above the attachment of the other three whorls,I,e, the corolla,calyx and androecium,the ovary is said to be superior ovary and the condition is known as HYPOGYNY.Such flowers are called hypogynous flowers. Example, China rose, mustard,citrus etc.
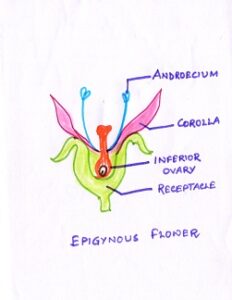
Fig#11 diagram of epigynous flower
(non flowering plant)
EPIGYNY :–(THE INFERIOR OVARY) If ovary is below the level of attachment of the three whorls,and the receptacle completely grows around the ovary,it is called inferior ovary and the condition is known as EPYGYNY.Such flowers are called Epygynous flowers,example : Sunflower, cucumber etc. ( synandrous stamen)
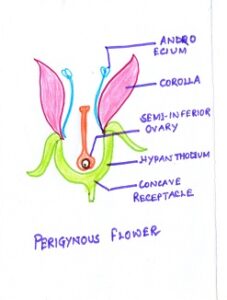
Fig#12 diagram of perigynous flower
PERIGYNY:-(THE INTERMEDIATE OVARY OR HALF INFERIOR OVARY) If the ovary is surrounded by a receptacle which grows to form a cup-shaped structure uo to the midway of the ovary and the other three whorls sprout from the receptacle rim,the ovary is said to be HALF-INFERIOR, or INTERMEDIATE. Such condition is known as perigynia and the flowers are called perigynous flowers. Example, : Pea,been etc. ( ———— are the non-essential parts of a flower)
INFLORESCENCE-ARRANGEMENT OF FLOWERS ON FLORAL STEM.
(non flowering plant)
An INFLORESCENCE is an arrangement of group or cluster of flowers on a branch of a plant. Inflorescence refers to the way of individual flowers arranged on the axis or floral stem or rachis. (synandrous stamen)
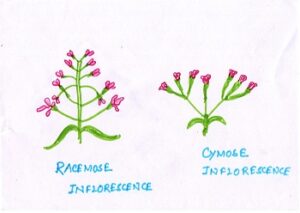
Fig#13 diagram of racemose and cymose inflorescence
(non flowering plant)
Depending upon the arrangement of flowers on the axis, or peduncle may be branched may be branched or or unbranched. The Inflorescence is of two types—racemose and cymose about which you may know afterwards.