ALLOTROPY
INTRODUCTION
It is the property by which an element exists in more than one form and each form had different physical properties but identical chemical properties. Elements having these different properties are allotropes. The characteristics of the elements we term as allotropy.
ELEMENT SHOWING ALLOTROPY AND CATENATION
Carbon exists in different allotropic forms. Some of them are
- Crystalline forms like diamond, graphite and fullerene.
- Micro-crystalline form or amorphous form like coal, lampblack, charcoal.
VERSATILE NATURE OF CARBON IN ALLOTROPY [CATENATION]
The estimated number of carbon compounds what we know today, is about three millions. We can raise the question that, which properties of carbon are responsible for the formation of such a large number of carbon compounds. Main factors that enables carbon to form large number of compounds in allotropy are:
- CATENATION : Carbon atoms binds each other by covalent bond in catenation. This bond is a long with straight or branched chains. They form rings of different sizes. This property of catenation we term as catenation. Carbon allows maximum catenation in the periodic table due to its small size. This enables the nucleus to hold on to the shared pairs of electrons strongly and C-C bond becomes strong.
- TETRAVALENCY OF CARBON : In periodic table group 14 is the position of Carbon. Its atomic number is 6 and the electronic configuration is 2,4. Thus it has 4 electrons in the outermost shell. Hence, its valency is four. That means it is capable of bonding or pairing with four other carbon atoms. It can also pair up with monovalent elements like hydrogen, halogen like chlorine, bromine.
- TENDENCY TO FORM MULTIPLE BONDS: Carbon has a strong tendency to form multiple bonds like double bond or triple bond due to its small size. It is possible by sharing more than one electron pair with its own atoms or with the atoms of elements like oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur etc. For this reason, carbon can form very stable compounds with these elements.
VARIOUS TYPES OF ALLOTROPES IN CATENATION
DIAMOND
General properties
- It is a colorless transparent substance with extra ordinary brilliance due to its high refractive index.
- It is quite heavy.
- It is the hardest natural substance.
- It does not conduct electricity as no free electrons are present in this substance.
- It has high thermal conductivity and high melting point.
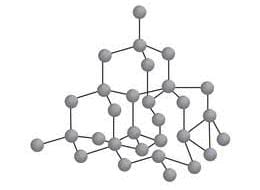
STRUCTURE
IN CATENATION
It is a giant molecule of carbon atom. Here each atom is bonded to four other carbon atoms forming a rigid three dimensional network structure. It is responsible for its hardness. There needs a lot of energy to break the network of strong covalent bonds in the diamond crystal.
GRAPHITE
IN CATENATION
General properties
- It is a grayish black and opaque substance.
- It is lighter than diamond.
- It is smooth and slippery in touch.
- Graphite is a good conductor of electricity due to presence of free electrons.
- But it is a bad conductor of heat.
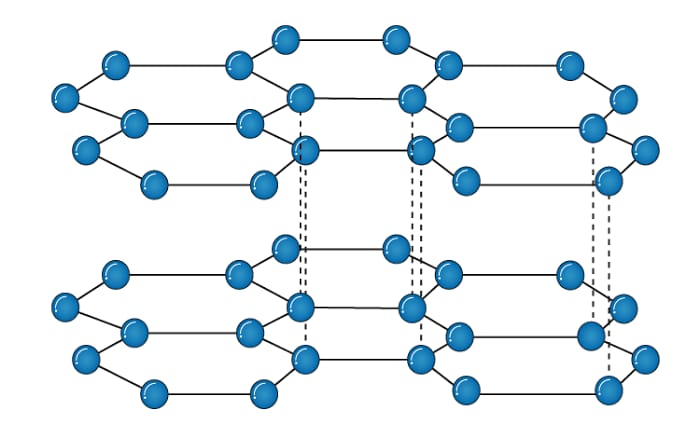
STRUCTURE
A graphite crystal consists of layers of carbon atoms. Each carbon in graphite layer is joined to three other carbon atoms by strong covalent bonds to form flat hexagonal rings. However,the fourth electron of each carbon atom is free. This free electron enables graphite to make good conductor of electricity. The various layers of carbon atoms in graphite held together by weak Van der Waal’s forces. For this reason it can slide over one another and therefore, graphite is slippery to touch.
FULLERENES
General properties and structure
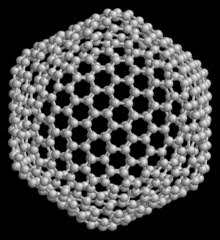
This allotropic form was recently discovered . First time H.W. Kroto and Robert Curt prepared this form by the action of laser beam on the vapor of graphite. The first known fullerene is C60 which contains 60 carbon atoms. In this form, arrangement of carbon atom is similar to the shape of football containting 60 to 370 carbon atoms. Fullerene was named BUCKMINSTER FULLERENE due to their resemblance in structure with geodesic dome. This dome was designed and built by the American Architect Robert Buckminster Fuller.
QUESTIONS RELATED TO ALLOTROPY AND CATENATION
Qs1: How can one make artificial diamond?
Ans1: Anyone can make diamond artificially by subjecting pure carbon in very high pressure and temperature. These synthetic diamonds are small but indistinguishable from natural diamomd.
Qs2: Name some other elements showing the property of catenation. Is this property of catenation for those elements stable?
Ans2: Elements other than carbon like sulphur, silicon also have a tendency to show the property of self linking i.e. catenation. But there is less bond energy or strength in catenation. So the bond formed by elements having atoms in cateenation are weaker and not stable.
Qs3: Diamond and graphite show different physical properties although they are made up of carbon. Name this relationship between diamond and graphite. Discuss about the basis of their relationship also.
Ans3: Relationship between diamond and graphite we term as allotropy. The physical properties are different among themselves. It is due to carbon-carbon bonding in both allotropes are different.
Diamond is hard because in it one carbon atom is bonded with four other carbon atoms with strong covalent bond. But in graphite , it is soft in texture. Here carbon atom is joined to three other C atoms by strong covalent bonds to form flat hexagonal rings.
The various layers of C-atoms in graphite are quite far apart, so that covalent bonds can exist between them the various layers of carbon atom in graphite are held together by weak Van der Waal’s force. So, they can slide over one another.
Qs4: State the reason why carbon atom can neither form C4+ cations nor C4- anions but forms covalent compounds?
Ans4: Atomic number of carbon is six. We can understand that outermost shell has four electrons. To get noble gas electronic configuration ,more four electrons are needed. It does not form carbon cation as the removal of four valence electrons will require a huge amount of enery.
The positive ion contains 6 positively charged protons and 2 negatively charged electrons. This makes it highly unstable. Carbon is unable to form carbon anion as its nucleus with six protons will not be able to hold ten electrons due to its small size. In this way, with same or different other atoms carbon atom can get octate configuration by sharing their four electrons. That is why it forms covalent compounds.